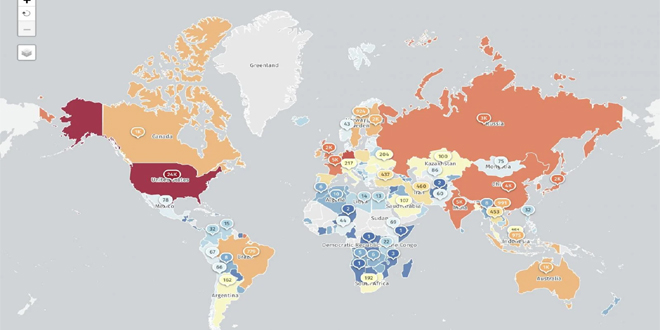
Mais de 77.000 endereços IP online estão em risco devido à grave falha de execução remota de código do React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182). Pesquisadores relatam que atacantes já invadiram mais de 30 organizações em vários setores.
React2Shell é uma vulnerabilidade que permite a execução remota não autorizada de código com apenas uma requisição HTTP. Ele afeta todos os frameworks que utilizam Componentes do Servidor React, incluindo Next.js, devido à lógica compartilhada de desserialização.
Em 4 de dezembro, o pesquisador de segurança Maple3142 lançou uma prova de conceito para execução remota de comandos em servidores não atualizados. Isso levou à varredura rápida da vulnerabilidade, já que tanto atacantes quanto pesquisadores utilizaram o exploit público com automação.
Mais de 77.000 endereços IP vulneráveis:
A Fundação Shadowserver tem fundar 77.664 endereços IP em risco devido à falha do React2Shell, incluindo cerca de 23.700 nos EUA.
Pesquisadores descobriram que endereços IP foram expostos a vulnerabilidades por meio de um método de detecção do Searchlight Cyber/Assetnote, que envolvia enviar uma requisição HTTP para servidores para explorar uma falha e verificar a resposta para confirmar a vulnerabilidade do dispositivo.
GreyNoise detectou 181 único IP Endereços tentando explorar a falha nas últimas 24 horas, principalmente por tráfego automatizado. A maioria dos exames vem da Holanda, China, Estados Unidos, Hong Kong, e alguns outros países.
A Palo Alto Networks revela que mais de 30 organizações foram afetadas pela falha do React2Shell, permitindo que atacantes executem comandos, coletem informações e tentem roubar arquivos de configuração e credenciais da AWS.
Esses compromissos incluem intrusões ligadas a atores chineses conhecidos associados ao Estado.
Empresas ao redor do mundo instalaram rapidamente o patch e aplicaram correções para a grave falha do React.
Ontem, a Cloudflare implementou medidas emergenciais para a falha React em seu Web Application Firewall (WAF) devido à sua séria exploração.
No entanto, a atualização causou inadvertidamente uma queda que afetou vários sites antes que as regras fossem corrigidas.
A CISA incluiu o CVE-2025-55182 no catálogo de Vulnerabilidades Exploradas Conhecidas, exigindo que as agências federais o corrigam até 26 de dezembro de 2025, conforme a Diretiva Operacional Vinculativa 22-01.
Organizações que utilizam Componentes de Servidor React ou frameworks relacionados devem atualizar imediatamente, reconstruir e reimplantar suas aplicações, e verificar logs para atividade de comandos PowerShell ou shell.